Hello, this is Nakasaki from the Sales Department at Vauldex.
In recent years, blockchain technology has gradually expanded beyond its origins in cryptocurrency and into broader areas of society. What first gained attention as the underlying mechanism for digital assets is now being applied in fields such as art, music, tickets, contracts, and membership certificates.
Alongside this shift, the term NFT (Non-Fungible Token) has become increasingly common. An NFT is a mechanism that gives digital data a sense of uniqueness, making it possible to verify who owns it and whether it is authentic. The way we handle digital data, once assumed to be infinitely copyable, is beginning to change.
This transformation is not limited to art and entertainment. It is spreading into areas that require reliable verification, such as digital contracts, warranties, and identity credentials. As a society, we are entering a phase where we must rethink how proof and certification are handled in digital form.
The diploma is a natural extension of this discussion within the field of education. Diplomas are essential documents required at major milestones in life, such as entering higher education or applying for employment. In response, efforts are gradually emerging to reconsider how diplomas are managed, using blockchain and NFT technologies. When people hear the phrase “NFT diploma,” it can sound technical or premature for their institution. Many are interested, yet unsure where to begin.
In this article, we will organize the background and key perspectives that educational institutions should understand when considering NFT diplomas. Before diving into technical details, we begin by asking: What is happening now, and why is this becoming a topic worth examining?
Table of Contents
- What Is an NFT, and Why Does It Fit Diplomas?
- Current Practices and Their Small Frictions
- Social Trends and the Role of Education
- Early Adoption Cases
- Benefits of Introducing NFTs
- Key Considerations for Educational Institutions
- Future Outlook
What Is an NFT, and Why Does It Fit Diplomas?
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token, a blockchain-based mechanism that guarantees the uniqueness of data. Although it may sound technical, the core idea is simple. Traditional digital data can be easily copied or modified, making it difficult to determine which version is the original. For example, a PDF diploma may look identical to the original, but it can be difficult for a third party to verify its authenticity.
NFTs change this premise. They allow verification of who owns the data, who issued it, and whether it has been altered. In other words, NFTs enable digital data to be recognized as authentically owned and verifiable.
Diplomas align well with this technology because they are inherently issued only once per individual and highly dependent on authenticity. NFTs provide a natural way to replicate these characteristics in the digital world.
For example, when applying to study abroad or to a graduate program overseas, applicants traditionally must mail paper documents or undergo certification procedures, often taking weeks. With blockchain-based verification, authenticity can potentially be confirmed instantly via a shared link.
In practice, NFTs alone are not sufficient. Typically, NFTs verify ownership and transferability of the diploma data, while Verifiable Credentials (VCs) ensure the authenticity of the academic information itself. Together, these technologies enable practical digital diploma systems.
Current Practices and Their Small Frictions
Most educational institutions today issue diplomas on paper, sometimes supplemented by PDF versions. This system has functioned reliably for decades and remains socially accepted.
However, when we look closely at real-world usage, several small but recurring frictions emerge.
First, timing after graduation. Diplomas are often required at critical moments, such as job applications, licensing, study abroad, or graduate admissions. Paper documents require reissuance and mailing. PDFs may be misplaced or difficult to locate quickly.
Second, the risk of academic fraud. While not frequent in Japan, internationally there have been cases of fraudulent degree certificates, often referred to as diploma mills. As verification expectations increase globally, institutions must be prepared to respond.
Third, administrative burden. Issuing and responding to verification requests typically depends on manual administrative processes. While manageable under normal circumstances, workloads often spike during graduation season or busy periods.
For example, one graduate of a Japanese university needed a diploma for overseas graduate applications. Reissuing a paper certificate would have taken several weeks, while the deadline was imminent. Although they ultimately met the deadline, they later reflected that arranging documentation consumed valuable time that could have been spent on their research proposal.
These are not catastrophic flaws. However, as society digitizes and cross-border mobility increases, such frictions become more visible. The question is not whether the current system is bad, but whether it can evolve alongside changing needs.
Social Trends and the Role of Education
Across society, digitization and AI adoption are accelerating. Processes once conducted in person or on paper are increasingly completed online.
Verification is no exception. Job applications and study abroad procedures are now largely digital. International standards such as Verifiable Credentials are being developed and tested worldwide.
Other industries have already transitioned to blockchain-based verification systems for tickets, warranties, and membership cards. It is not unnatural for education to follow.
In the future, the value of certification may be judged not only by whether it exists, but by how smoothly it can be obtained, presented, and verified. Educational institutions must consider how they will provide proof of learning within this evolving environment.
Early Adoption Cases
Several institutions have already begun implementing NFT- or VC-based diploma systems.
- At MIT in the United States, the university has used the Blockcerts system since 2017. Graduates can self-custody their credentials, and third parties can verify authenticity via URL. Thousands of graduates have participated.
- In Japan, the Chiba Institute of Technology began pilot programs issuing digital graduation certificates in 2021, becoming one of the early domestic examples.
- In Europe and Asia, some universities are conducting pilot programs involving tens of thousands of graduates, anticipating international submission and usage.
A common thread among these initiatives is the concept that students own their credentials and can present them when needed. This reflects a broader shift in how educational proof is conceived.
Benefits of Introducing NFT Diplomas
Through discussions with educational institutions, three key benefits consistently emerge.
The first is trust and security. Tamper-resistant mechanisms ensure credibility, and recipients can verify authenticity instantly.
The second is efficiency. Issuance, verification, and re-acquisition can be handled online, reducing administrative burden.
The third is expandability. By aligning with international standards, institutions can support overseas submissions and potentially integrate with broader learning records and skill certifications.
These benefits extend beyond operational efficiency. They enhance the intrinsic value of educational certification itself.
Key Considerations for Implementation
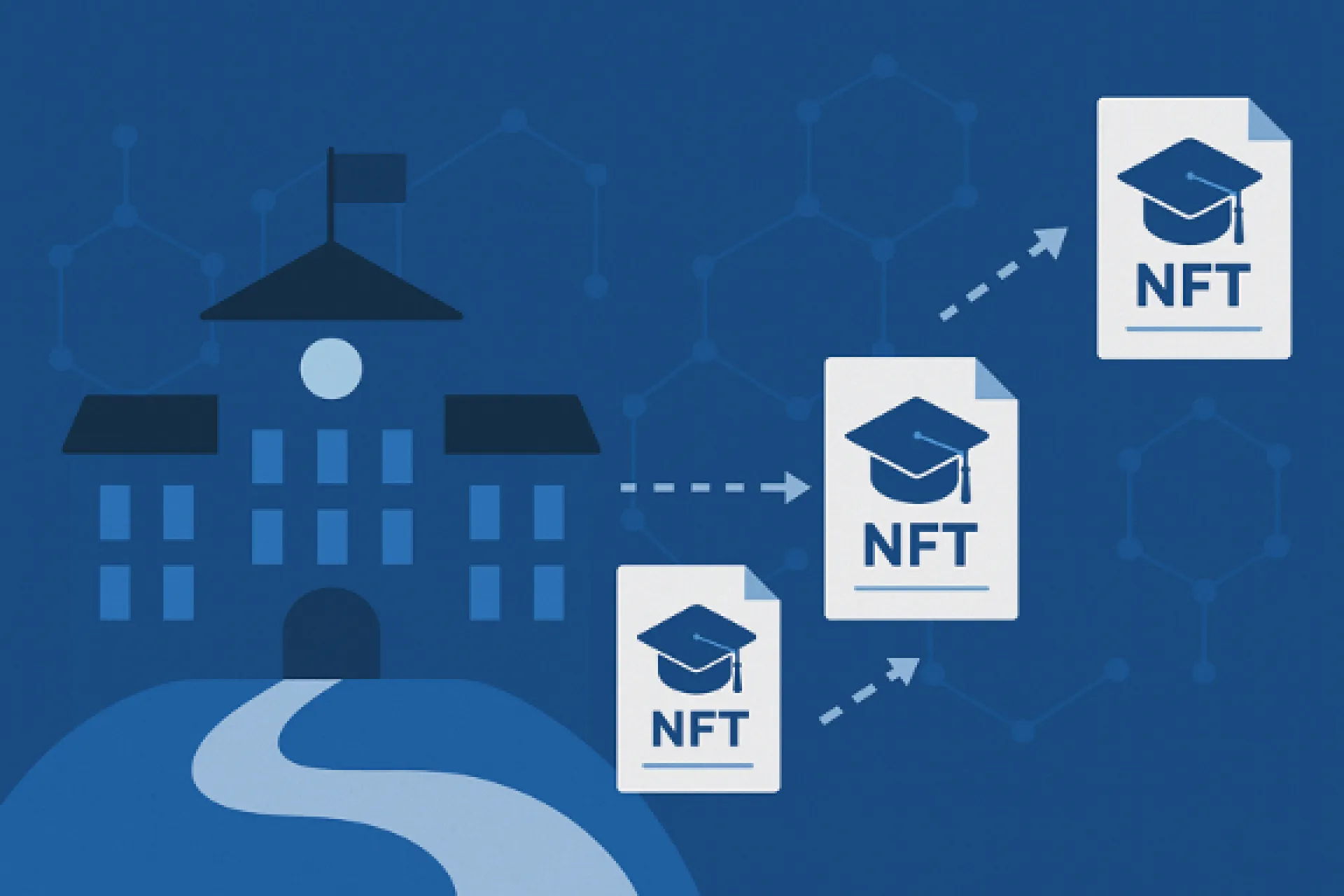
Over the next several years, digital diplomas are likely to become increasingly common. International pilot programs suggest that NFT diplomas may move beyond experimental cases and become recognized as a practical option.
That said, institutions need not implement them at full scale immediately. A realistic approach is to begin with a specific department, short-term programs, or specialized courses. Gradual implementation allows institutions to identify operational challenges and adapt the system to their context.
Looking ahead, NFT diplomas may evolve into comprehensive learning records, encompassing coursework completion, skill certifications, and extracurricular achievements. This would allow students to present their academic journey in a more structured and reliable manner, supporting career development while enhancing institutional brand value.
Furthermore, digital certification may expand equitable access. Students in regions where mailing physical documents is difficult, or international students crossing borders, could benefit significantly from instant, trusted verification.
The Future of Diplomas
Given the rapid pace of technological change, it is entirely possible that NFT diplomas will become a standard option within a few years.
From that perspective, asking today how an institution might adopt this approach and what preparation would be required is not premature. It is forward-looking.
As technology and society evolve, the very concept of a diploma may be reconsidered. Beginning to organize information and reflect on these developments now is a meaningful step toward fulfilling education’s responsibility to support students’ futures.
We may be at a moment when the technology is mature enough to consider seriously, yet early enough to shape thoughtfully.
If you would like, I can also refine this into a more academic tone, a more persuasive marketing version, or an SEO-optimized web article.

